Project Overview
At Datraxa, we developed an advanced urban sound classification deep learning machine learning system that identifies and categorizes city sounds using both neural networks and traditional algorithms. The goal was to combine the strengths of both methods for accurate and efficient sound recognition.
This project explores how deep learning detects patterns in sound spectrograms while machine learning processes structured audio data. Together, they enhance the accuracy and interpretability of sound recognition models.
Visit the UrbanSound8K dataset on Kaggle to learn more about the data used in this project.
Data and Methodology
We used the UrbanSound8K dataset, containing 8,732 audio clips labeled across ten sound classes, including car horns, drilling, and dog barks.
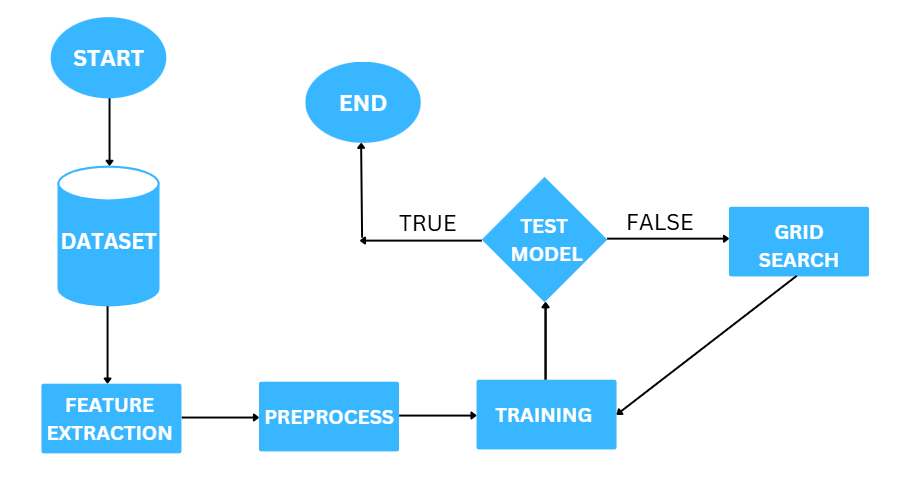
Deep Learning Track: Built a CNN model using melspectrograms as input images to identify audio patterns.
Machine Learning Track: Extracted features like MFCC, Chroma, and Spectral Flux, then trained models such as LightGBM, XGBoost, and Random Forest.
Hyperparameter tuning was done using Optuna for CNNs and GridSearchCV for LGBM. Both models were compared through A/B testing to evaluate their real-world accuracy and scalability.
For a related Datraxa AI project, check out our Time Series Forecasting System.
Results and Insights
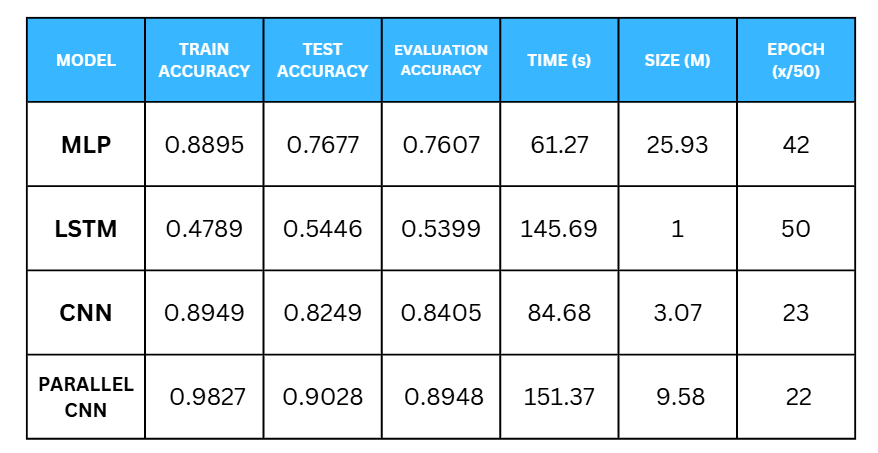
The CNN-based model achieved high precision in recognizing urban sound patterns, while LightGBM provided fast and interpretable results for tabular features. Adding a custom class named “Love” improved model diversity and emotion detection capabilities.
This urban sound classification deep learning machine learning pipeline proves how Datraxa combines innovation and data science to solve complex audio analysis challenges.
Deep Learning Pipeline
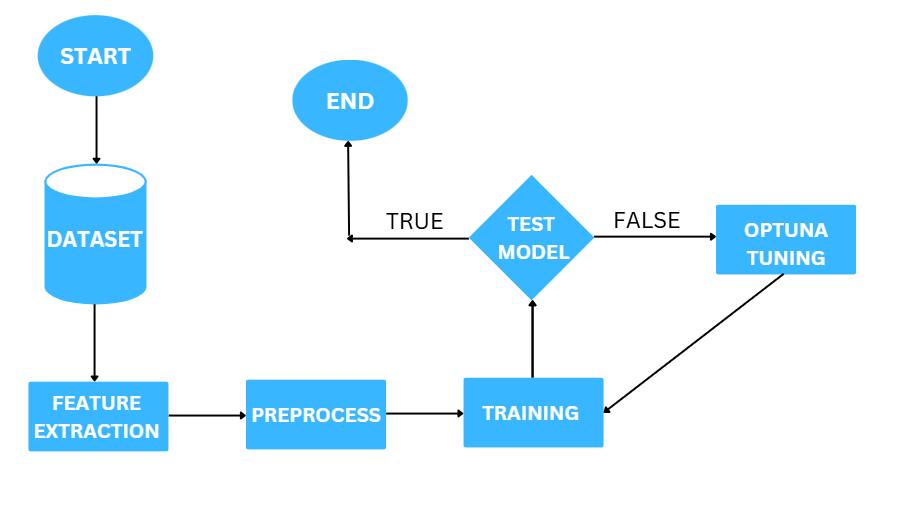
Machine Learning Pipeline